Wastewater Treatment
System
Waste water treatment
A water treatment plant in Pakistan is required for successful wastewater management. Midwater offers advanced methods for purifying industrial and domestic wastewater, resulting in clean and safe water for use or waste. Our important solutions remove contaminants, protect the environment, and maintain legal regulations. With increasing water contamination, a dependable wastewater treatment system is vital. Midwater offers innovative, budget-friendly, and eco-friendly water treatment solutions across Pakistan.
Wastewater Treatment Removes The Following Issues:
- Elevated discharge volume
- Elevated BOD levels
- Elevated TDS or TSS levels
- Elevated phosphate or nitrate levels
- Harmful substances in waste stream
- Dynamic compliance procedures


MEMBRANE BIOREACTOR TECHNOLOGY
Membrane bioreactor (MBR) technology is an integration of biological treatment and membrane filtration into a single process, in which microorganisms are responsible for organic and nitrogen removal, while membranes capture biomass and suspended solids physically from the mixed liquor. The MBR process utilizes microfiltration cartridges (MF) or ultrafiltration (UF) technology ranging from 0.05 to 0.4 µm to enable complete retention of bacterial flocs and suspended solids. MF membranes are responsible for removing suspended solids, algae, protozoa, and bacteria, while UF membranes an additionally retain small colloids and viruses.
The configuration of membrane plays a crucial role in determining the process performance. There are mainly three types of membrane configurations that are being used in MBR technologies: 1) plate-and-frame/flat sheet (FS), 2) hollow fiber (HF), and 3) multi tubular (MT). In FS membranes, the fluid flows from the membrane’s coated side towards the permeate side. In MT module, fluid flows from inside towards outside the tube (lumen to shell-side), whereas in HF configuration fluid flows from outside towards inside (shell to lumen-side).
Main Stages Of The Wastewater Treatment Process
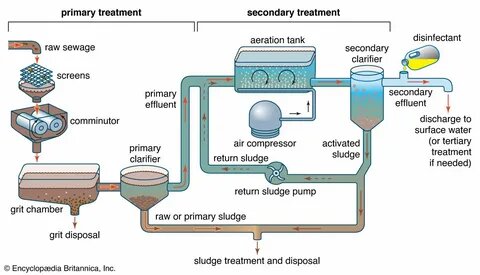
Secondary Treatment
In secondary treatment, the wastewater is pumped into tanks containing bacteria that break down waste products into less harmful substances. Once this process is complete, remaining solids are removed. In further digestion process, sludge breaks down into inert biosolids which are pumped to holding lagoons. Produced methane gas is burned in boilers to heat the digestion process. Yearly, the biosolids are spread on farmland as organic fertilizer.
How Does A Wastewater Treatment Plant Work?
How Does A Wastewater Treatment Plant Work?

MIDWATER Wastewater Treatment Plant
In nature, bacteria feed on organic waste and break the main stages of the wastewater treatment process it down into less harmful substances. In Midwater, sewage, or wastewater, goes to the Wastewater Treatment Plant (WWTP). At the plant, natural biological processes are accelerated and combined with physical and chemical treatment processes to remove undesirable solids and microorganisms before the water is recycled back into the Midwater.
Midwater’s WWTP is regulated through approval from Alberta Environment. Samples are taken as wastewater enters and leaves the WWTP. An on-site laboratory then analyzes the samples to determine the plant’s efficiency and make sure The City is meeting government regulations. This ensures strict environmental guidelines are met.
How does a wastewater treatment plant work?
Pretreatment Screening
The pretreatment phase involves filtering large waste materials from the water. The rate of water inflow is also monitored in order to separate organic materials such as sand, glass, and stone.


Wastewater Aeration
After pretreatment, the process of aeration is used to supply oxygen to bacteria for purifying and preserving the wastewater. This development allows for biodegradation, which dissolves the organic substances that contain carbon into smaller compounds to form CO2 and water.
Primary Treatment
Primary treatment consists of the usage of equipment to break down large contaminants. Afterwards, extracting these contaminants is undertaken through the use of sedimentation. Secondary treatment is usually used alongside the primary method for the purposes of further removing organic matter

Post Treatment
Chlorination dosing and UV purification systems are widely used methods to remove harmful microorganisms in water. Chlorine has gained its popularity due to its effectiveness in eradicating disease-causing bacteria.

